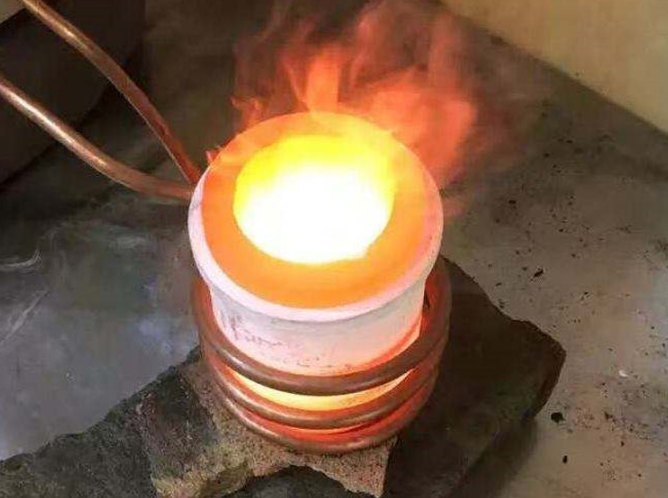
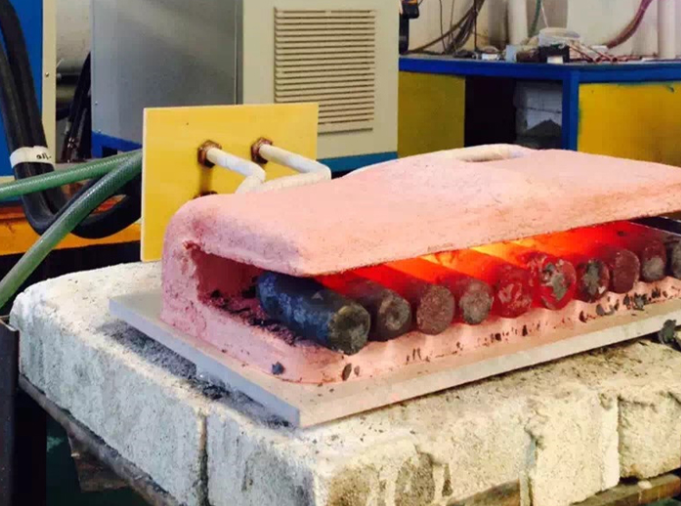
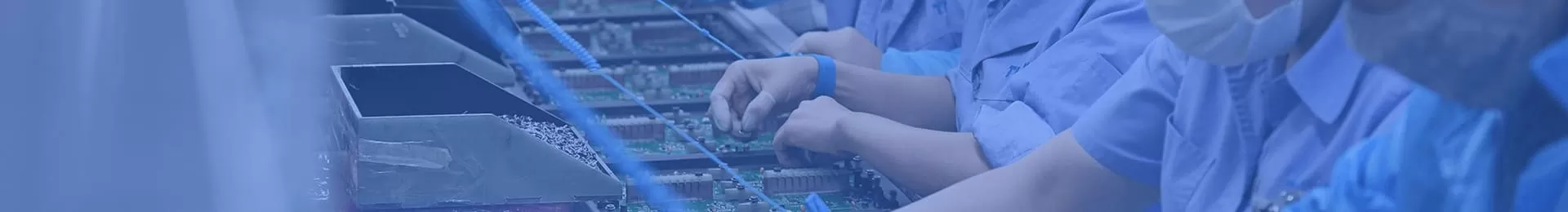
A bearing heater is a device used to heat bearings prior to mounting or dismounting them. Because bearings vary widely in size and design, there is no “one size fits all” method for installation. This makes bearing heaters essential tools, allowing bearings to be heated so they can slide onto a shaft with minimal force and without the risk of damage.
Proper installation has a direct impact on bearing performance, service life, and durability. Bearing heaters help prevent misalignment during installation by heating the inner ring and causing it to thermally expand, enabling smooth and accurate mounting. They are commonly used for small to medium-sized bearings such as roller bearings, ball bearings, spherical roller bearings, cylindrical roller bearings, tapered roller bearings, and more.
Controlled Heating in Bearing Installation – How It Reduces Damage & Improves Efficiency
Bearing heaters are equipped with temperature sensors that monitor the bearing’s temperature throughout the heating process. Many models also include adjustable thermostats to prevent overheating. Controlled heating improves installation quality and efficiency for several key reasons:
1.Prevents Overheating and Bearing Damage
Excessive heat can alter the bearing’s metallurgy, affecting hardness and significantly reducing service life. Controlled heating keeps the temperature within the manufacturer’s recommended range to avoid these risks.
2. Reduces Installation Force & Protects the Shaft
By expanding the inner ring uniformly, bearing heaters eliminate the need for cold mounting methods that rely on force. This prevents damage to the shaft and bearing race—common problems when bearings are hammered or pressed into place.
3. Ensures Even Thermal Expansion
Compared with ovens or open flames, bearing heaters provide consistent, uniform heating. This ensures that the bearing expands evenly, preventing distortion, warping, or misalignment during installation.
4. Enables Faster and Safer Installation
Controlled heating shortens mounting time and minimizes the chance of worker injury or shaft damage. Many heaters automatically regulate temperature and alert the operator when the bearing is ready, helping avoid overheating and installation errors.
5. Maintains Lubricant Integrity
Uneven or excessive heating can degrade or burn off lubricants, increasing friction and shortening bearing life. Controlled heating ensures that pre-greased bearings maintain their lubricant properties and overall performance.
Why Use a Bearing Heater?
Bearing heaters are used to thermally expand a bearing so it can be mounted or dismounted without excessive force or cold installation methods. This controlled expansion prevents damage to both the bearing and the shaft. Bearing heaters are commonly used for:
Mounting: Heating bearings so they can be easily mounted onto shafts, gears, and other machine components.
Dismounting: Expanding bearings to safely remove them from shafts, gears, and other components without mechanical force.
Heating Other Components: Also suitable for heating gears, pulleys, bushings, and similar shrink-fit parts.
Advantages of Using a Bearing Heater
Controlled Heating: The primary benefit of a bearing heater is its precise temperature control. It maintains a safe, predefined temperature to prevent metallurgical damage and ensures the bearing is heated to the optimal level required for proper installation.
Reduced Bearing Damage: By eliminating the need for mechanical force—such as hammering or pressing—bearing heaters help prevent brinelling, cracking, distortion, and misalignment during mounting.
Faster & More Efficient Installation: Bearing heaters warm bearings quickly, enabling faster installations, reducing equipment downtime, and minimizing the need for manual force. This also helps reduce operator fatigue and improves overall workflow efficiency.
Safer Operation: Compared to traditional heating methods like open-flame torches, bearing heaters offer a significantly safer solution. They eliminate fire hazards, and built-in sensors help prevent overheating and ensure safe operation.
Extended Bearing Life & Performance: Controlled heating prevents microcracks, distortion, and other damage that can lead to premature bearing failure. It also protects pre-applied lubricants from burning off, helping maintain proper lubrication and long-term performance.
Types of Bearing Heaters
There are several types of bearing heaters available, each designed for different heating methods, efficiency levels, and application sizes. The most common types include:
Induction Bearing Heater: These heaters use electromagnetic induction to heat the bearing. They are the most widely used type and typically feature a yoke that is inserted through the bearing bore to deliver uniform, controlled heating.
Hot Plate Bearing Heater: Hot plate heaters rely on conduction heating. The bearing is placed directly on a heated metal surface. These heaters are generally preferred for small bearings and applications where simple, direct heating is sufficient.
Cone-Style Bearing Heaters: As the name suggests, cone-style heaters are cone-shaped and designed to accommodate a range of bearing sizes. Heat is transferred through the cone into the bearing’s inner ring, making them useful for quick, localized heating.
How to Choose the Right Bearing Heater
The saying “different situations call for different approaches” applies directly to selecting the right bearing heater. Several factors determine which heater is best suited for your application. Key considerations include:
Bearing Size & Type: Choose a bearing heater based on the size and design of the bearing. Smaller bearings—such as small deep groove ball bearings—are often heated with hot plate heaters. Larger bearings, like spherical roller bearings, typically require an induction heater for efficient and uniform heating.
Heating Method: Select the heater according to your heating requirements. Induction heaters provide rapid heating and are ideal for high-production environments where quick mounting is essential. Hot plate heaters offer slower, more controlled heating and are suitable for small bearings or applications where gradual temperature increase is preferred.
Application Environment: The environment in which the heater will be used is an important factor. Portable induction heaters are ideal for field service and on-site maintenance, while stationary units are better suited for workshop or repair-shop settings.
Energy Efficiency: Energy consumption should also be considered. Induction heaters generally use less power than hot plate heaters, making them a more efficient option for frequent or high-volume bearing installations.
Applications of Bearing Heaters in Different Industries
| Industry | Application |
| Automobiles | Mounting bearings in engines, wheel hubs, etc. |
| Power Generation | Installing bearings in turbines, generators, and more. |
| Aerospace | Fitting bearings in landing gears, shafts, and engines. |
| Railways | Fitting large bearings in locomotives and rolling stock. |
| Manufacturing | Mounting bearings on machine tools, conveyor belts, etc. |
Accessories for Bearing Heaters
Heat Protective Gloves: Handling bearings before and after heating requires proper hand protection. Heat-protective gloves help prevent burns and also protect the bearings from scratches or accidental damage during handling.
Bearing Puller: A bearing puller is used to remove bearings from shafts, housings, and other mechanical components. It ensures that parts are extracted without damage. Bearing pullers are designed to operate effectively in confined spaces, allowing technicians to remove bearings, gears, pulleys, and similar components while minimizing the risk of harming surrounding parts and reducing machine downtime.
Temperature Monitoring Tool: Tools such as infrared thermometers are used to measure the bearing temperature and prevent overheating. Many advanced bearing heaters come equipped with built-in digital thermometers and temperature displays for better control during heating.
Supportive Accessories: Spacer rings, support blocks, alignment tools, centering devices, and other accessories are often used to ensure proper heating, accurate installation, and reduced downtime during maintenance or assembly procedures.
FAQs
What is a bearing heater used for?
A bearing heater is used to heat bearings before mounting or dismounting them. Heating expands the bearing, allowing it to be installed or removed without excessive force.
What is the best way to heat a bearing?
The best and safest way to heat a bearing is by using a bearing heater. Bearing heaters offer controlled heating, work with a wide range of bearing sizes, and reduce the risk of damage during installation.
What are the common types of bearing heaters?
Common bearing heater types include induction bearing heaters, hot plate bearing heaters, and cone-style bearing heaters. Each type suits different bearing sizes and heating requirements.
Why do you heat bearings?
Bearings are heated to expand them, making it easier to mount or dismount them without the use of excessive mechanical force or cold methods that could cause damage.
What temperature should bearings be heated to?
A general guideline is 80–90°C, but the exact heating temperature should always follow the bearing manufacturer’s recommendations.