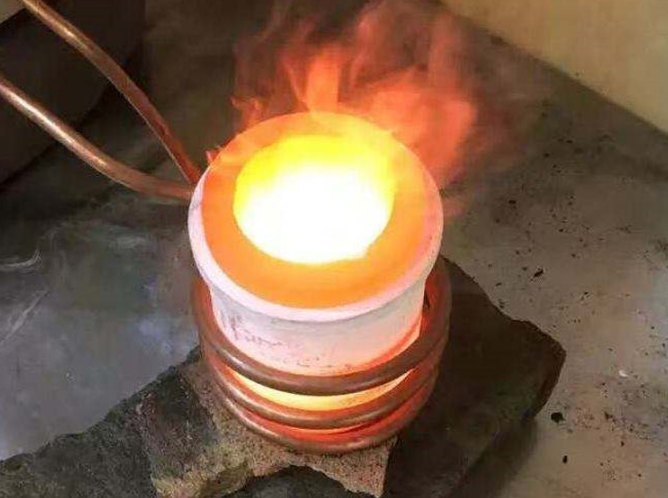
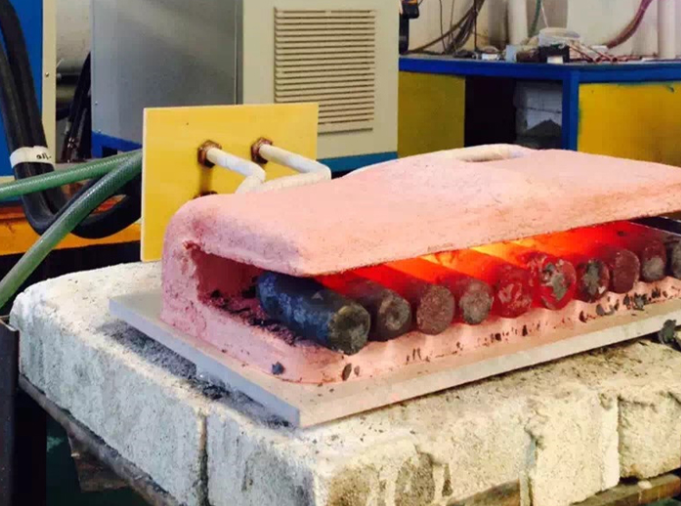
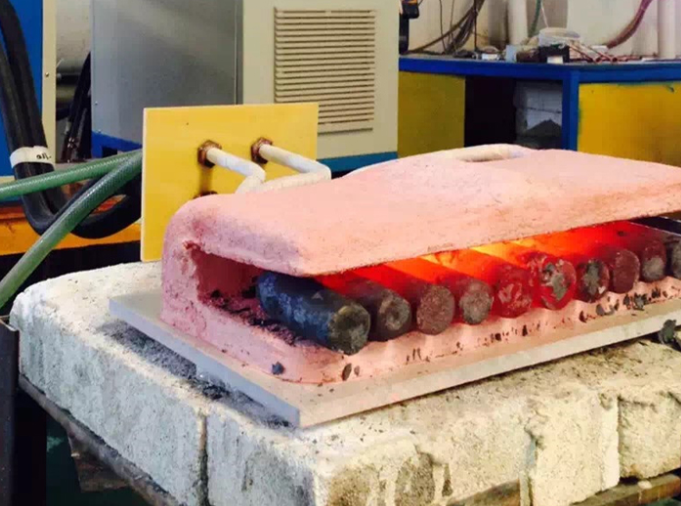
Induction heaters are increasingly popular in the manufacturing industry due to their high efficiency, low environmental impact, and ease of operation. They can safely perform a wide range of metalworking processes, including melting, brazing, and annealing.
An induction heater operates by using an alternating current to generate a magnetic field. This changing magnetic field induces eddy currents within a conductive material, which generate heat in accordance with the Joule heating law.
Induction heating has significantly influenced modern manufacturing by improving the efficiency and consistency of various production methods. One such application is the forging process, where induction heating plays a key role in enhancing process performance.

What Is Forging?
Forging is a metal shaping process that uses compressive forces to form a workpiece into a desired shape. These forces are typically applied using a hammer, press, or die.
Forging is one of the oldest metalworking techniques, historically used by goldsmiths to shape metals into functional and decorative objects. The process enhances several mechanical properties of the material, including strength, fatigue resistance, and impact resistance.
Hot and Cold Forging
Metal can be forged in two primary conditions: in its existing state at room temperature or after being heated above its recrystallization temperature.
When forging is carried out at room temperature without heating the metal, the process is known as cold forging. When the workpiece is heated to its recrystallization temperature before deformation, the process is referred to as hot forging.
Cold forging is commonly used for relatively softer metals, as it increases hardness and strength through deformation. In contrast, hot forging is suitable for nearly all types of metals and is more widely used in industrial applications, as heating allows for easier deformation and more precise shaping.
Use of Induction Heaters for Metal Forging
As discussed earlier, hot forging requires the metal to be heated before deformation. Traditionally, this heating is achieved using fuel-fired furnaces that operate on combustible fuels such as gas. This method involves direct heating and produces fumes and emissions as a result of fuel combustion.
Induction heating offers an effective alternative to conventional furnace heating. For small-scale applications, such as knife making, an induction heater can be used, while large-scale industrial operations typically employ induction furnaces. In both cases, electrical power is used to heat the metal efficiently and without direct contact.
Main Steps Involved in Forging Metals by Induction Heating
The induction forging process can be divided into three main stages.
Preheating with an Induction Heater:
The first step is heating the workpiece, typically ingots, to the required forging temperature using an induction heater. At this temperature, the metal retains its overall shape but becomes sufficiently malleable to be formed under applied force.
Hammering:
Once the ingot reaches the forging temperature, it is placed on an anvil, which provides a flat and stable surface for shaping. The heated metal is then forged into the desired form through hammering or pressing, either manually or using mechanical equipment.
Quenching:
After the metal has been shaped, it is cooled to stabilize its structure. Cooling may be achieved through quenching or air cooling. Quenching involves rapidly cooling the metal in water or oil, which increases hardness and helps prevent damage during cooling. Air cooling is a slower process and does not significantly increase hardness.
Advantages of Induction Heaters for Forging Applications
Compared with conventional heating methods, induction heaters offer several clear advantages for forging operations. Some of the most notable benefits include:
Rapid heating: Induction heaters provide fast heating cycles, allowing metal to reach forging temperature in a short time.
Safe operation: They are safer to use and do not generate fumes or smoke, improving the working environment.
Uniform heating: Induction heating delivers even temperature distribution, helping to reduce forging time and improve consistency.
Precise control: Induction systems offer a high level of control over the heating process compared with traditional gas-fired furnaces.
Ease of automation: When induction heaters are used, the forging process can be easily integrated into automated production lines.
FAQs
What metals can be forged using induction heating?
Almost all types of metals can be forged with induction heaters, although heating efficiency varies depending on the material. Commonly forged metals include aluminum, brass, copper, iron, stainless steel, and titanium.
Furnace heating vs. induction heating: which is better?
Traditionally, gas-fired furnaces were used for preheating metals. These furnaces require significant setup time and must operate continuously once started, as they cannot be easily stopped and restarted. In contrast, induction heaters provide heat on demand. They offer precise control and can be started or stopped instantly, resulting in shorter production cycles and improved operational flexibility.
What are the limitations of induction forging?
Despite its many advantages, induction forging has certain limitations. First, the size of the workpiece is constrained by the capacity of the induction heater. Second, induction systems are relatively expensive. Third, they require a significant initial investment, including setup costs and a high-frequency power supply, which may not be feasible for all manufacturers.
Summary
Induction heaters provide an efficient and reliable solution for heating metals in hot forging applications. Their ability to heat metals quickly and uniformly reduces forging time and improves process efficiency. In addition, induction heating is environmentally friendly and safe to operate, as it does not produce harmful fumes or emissions.